Industrial Plug Socket Connector Precision Engineered By Nante
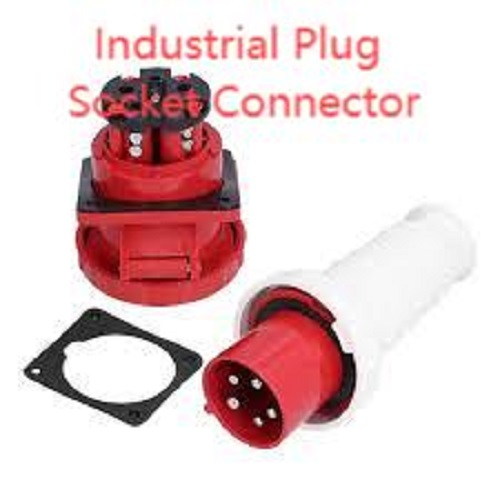

In demanding industrial environments, the right connectivity reduces unplanned stops and keeps production predictable. The Industrial Plug Socket Connector frequently serves as the primary interface between heavy equipment and supply, and choosing the correct family at specification saves both time and money. When evaluating new deployments, the Industrial Plug Socket Connector should be judged on contact metallurgy, mechanical retention, ingress protection, and ease of field servicing to ensure long-term operational reliability.
Specify for the real duty cycle
Start by quantifying how connectors will be used: mating cycles per shift, expected continuous current, peak loads, and frequency of disconnection. Components rated only for infrequent access will fail quickly when exposed to repeated plug/unplug actions. Specify a continuous-current rating above expected steady-state loads, and require mating-cycle data from vendors. For mobile tools or portable equipment, favor designs with robust retention systems and generous mechanical safety margins.
Contact technology, platings, and corrosion resistance
Contact materials and platings drive electrical performance. High-conductivity copper alloys with appropriate platings (silver, nickel, or gold flash) balance conductivity and corrosion resistance for specific atmospheres. In humid, marine, or sulfurous environments, gas-tight contacts and corrosion-resistant finishes slow resistance growth and lower thermal risks. Also consider contact cross-section — larger cross-sections dissipate heat better and reduce long-term resistive losses under heavy currents.
Mechanical retention, ergonomics, and mounting details
Choose coupling mechanisms that suit use: threaded couplings for vibration resistance, bayonet locks for quick changes, or keyed collars to prevent mis-mating. Design mountings so mechanical loads transfer to housing or backing plates rather than terminals, and use reinforced mounting bosses for thin panels. Ergonomic faceplates and clearly keyed inserts make operations faster and reduce human error during shift handovers.
Schneider-Compatible Accessories and retrofit options
Interoperability with common accessory ecosystems reduces spare-part variety and speeds upgrades. Schneider-compatible frames, surge modules, and locking covers let technicians swap modules or add protection without custom work. Retrofit-friendly footprints and standardized mounting patterns are especially valuable for phased modernizations, where preserving existing cutouts avoids costly panel modifications.
Installation best practices that prevent failures
Proper termination prevents most field faults. Require calibrated crimp tools and torque-controlled drivers for screw or stud connections; document torque values during commissioning. Route strain-relieved cable entries to avoid axial loads on contacts, and select correctly sized glands to preserve ingress ratings. A commissioning infrared thermal scan under representative load is invaluable — it identifies marginal crimps or undersized conductors before they cause trouble.
Testing, commissioning, and acceptance criteria
Beyond visual checks, mandate contact-resistance and insulation-resistance measurements and define acceptable thresholds. Use a short burn-in under expected load and follow-up thermal imaging to catch settling issues. Keep test records keyed to installation locations or serial numbers so recurring patterns indicate systemic issues, not one-off mistakes.
Spares strategy and field readiness
Optimize spare holdings by standardizing on one or two connector families across similar equipment. Keep replacement inserts, gaskets, coupling collars, and common fasteners in compact field kits so technicians can perform fast, controlled swaps. Favor vendor families with documented field-replaceable modules to reduce downtime and simplify repairs.
Predictive maintenance and telemetry opportunities
Small sensors — temperature probes, outlet current monitors, and insertion counters — turn connectors into early-warning points. Plan for mounting bosses and wiring channels during procurement so monitoring can be installed later with minimal disruption. Trend data on contact resistance or outlet temperature often reveals gradual deterioration long before functional failure.
Supplier selection and lifecycle cost thinking
Price is only one factor: weigh repairability, test-data, and aftermarket support. A low-cost sealed assembly that must be wholly replaced after damage can cost more than a repairable family with available spares. Request lifecycle test reports (mating cycles, salt spray, thermal aging) and prefer suppliers offering clear upgrade paths and field-replaceable parts.
Careful connector selection, disciplined installation, and a pragmatic spares and monitoring strategy convert a historically troublesome component into a managed asset that supports predictable production. For technical notes, accessory options, and detailed product information, see https://www.nante.com/news/industry-news/what-is-industrial-plug.html
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Oyunlar
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness